What Is Internal Linking in SEO?
Table of Contents
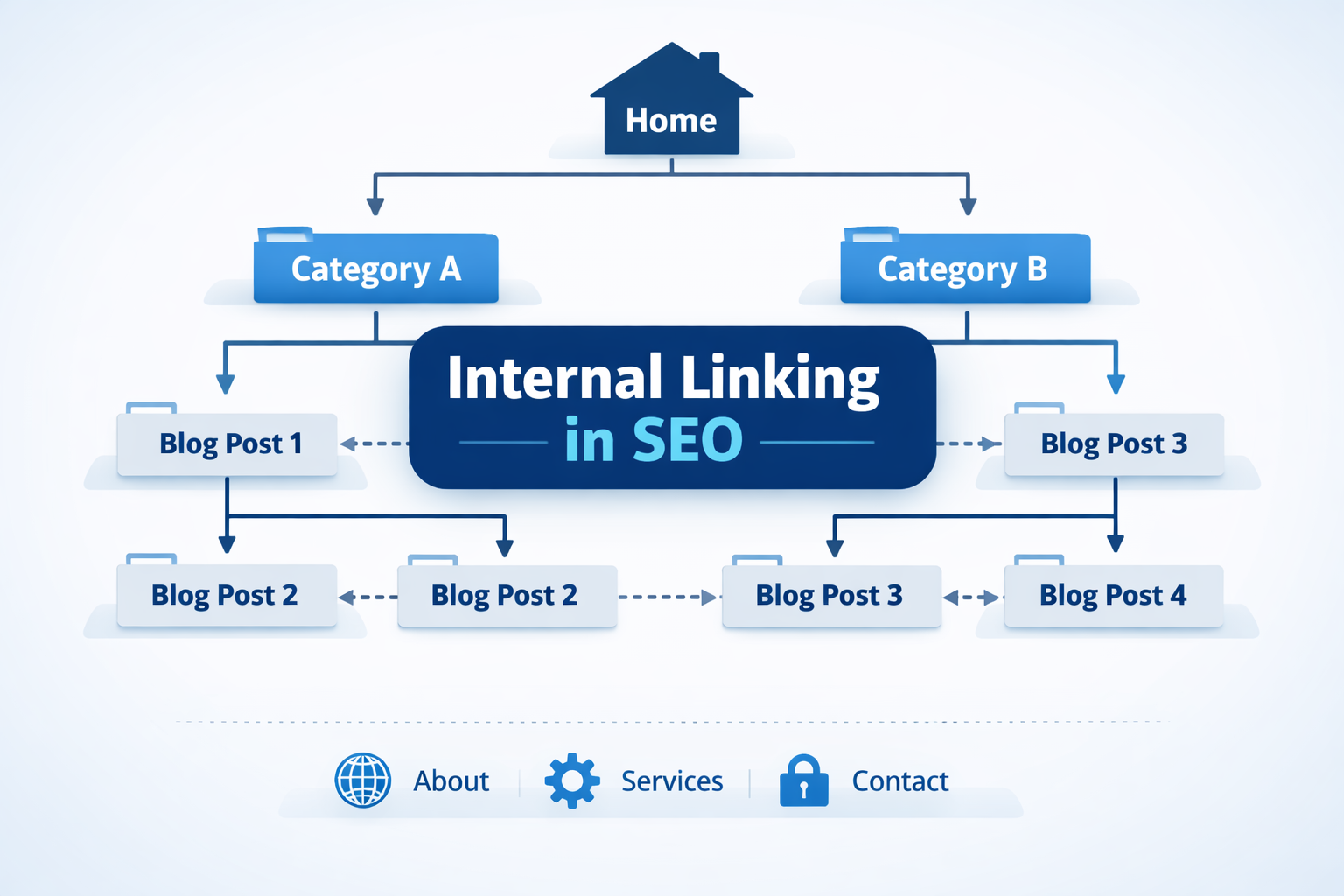
ToggleInternal linking in SEO is the process of linking one page of a website to another page on the same website.
It is done by using a keyword or phrase as anchor text, which helps users navigate to another relevant page within the site.

Why Is Internal Linking Important?
Internal linking is used to explain a concept in more detail by connecting to another relevant page on the same website. It helps provide additional information that supports the current page’s context.
Internal linking benefits both users and search engines. It creates a clear website structure and adds contextual value between related pages.
Proper internal linking also helps improve keyword rankings in search engines by distributing link value across pages.
Types of Internal Linking
1. Contextual Links
Contextual links are embedded within the main body of the content. These are the most valuable for SEO because they connect related topics and signal topical relevance to search engines.
2. Navigational Links
Navigational links are structural links usually placed in the top menu of a website. They help users access important pages such as the About page, Services page, or Contact page.
3. Footer Links
Footer links are located at the bottom of a webpage. They often contain links to legal pages, privacy policies, disclaimers, or sitemaps.
4. Sidebar Links
Sidebar links are positioned on the side of a webpage. They are commonly used to display recent posts, categories, or related articles to improve navigation.
5. Breadcrumb Links
Breadcrumb links are usually found at the top of a page. They show the user’s path within the site hierarchy, such as:
Home > Blog > Topic
They help improve navigation and enhance user experience.
6. Image Links
Image links are hyperlinked images, such as banners or images within an article, that direct users to another relevant page.
Best Practices for Internal Linking in SEO
Use descriptive anchor text: Internal links should use clear and descriptive keyword phrases as anchor text to explain the target page.
Place links within the content body: Internal linking is most effective when used naturally inside the main content.
Maintain a clear site hierarchy: Structure your website from top-down: Home > Categories > Subcategories > Posts.
Ensure pages are reachable: Make sure any target page can be accessed from the homepage within a few clicks.
Link from high-ranking pages to lower-ranking pages: Pages that already rank well should pass value to pages that need ranking improvement.
Limit excessive links: A few relevant, high-quality links are better than dozens of generic or low-value links.
Use do-follow and no-follow appropriately: Use do-follow links to pass authority. Use no-follow for pages you don’t want to rank, such as login or private pages.
Perform regular audits: Regularly check for broken links and update old content with new internal links to maintain link value.
Common Internal Linking Mistakes in SEO
Orphan Pages: Pages with no internal links pointing to them are difficult for users and search engines to discover and crawl.
Irrelevant Links: Linking to content that doesn’t fit the current page’s context can harm user experience and appear unnatural to search engines.
Over-Optimized Anchor Text: Using the exact-match keyword too often can appear spammy and may be flagged by search engines.
Non-Descriptive Anchor Text: Using phrases like “click here” or “read more” instead of descriptive phrases fails to inform users and search engines about the target page.
Broken Links and Redirects: Linking to 404 pages or creating redirect chains/loops wastes crawl budget and frustrates users.
Too Many Links on a Page: Overloading a single page with too many links dilutes authority and reduces SEO effectiveness.
Anchor Text Cannibalization: Using the same anchor text to link to different, non-relevant pages can confuse search engines about which page to rank.
Conclusion
After going through this blog on internal linking in SEO, it becomes easier to understand how internal linking helps users and Google in ranking. It also shows how mistakes like over-optimizing anchor text or using non-descriptive generic phrases do not provide much benefit.
Different types of links such as contextual links, footer links, sidebar links, and image links all help in creating connections between pages. This helps users spend more time on the website and get the desired information, which Google notices and considers in ranking.